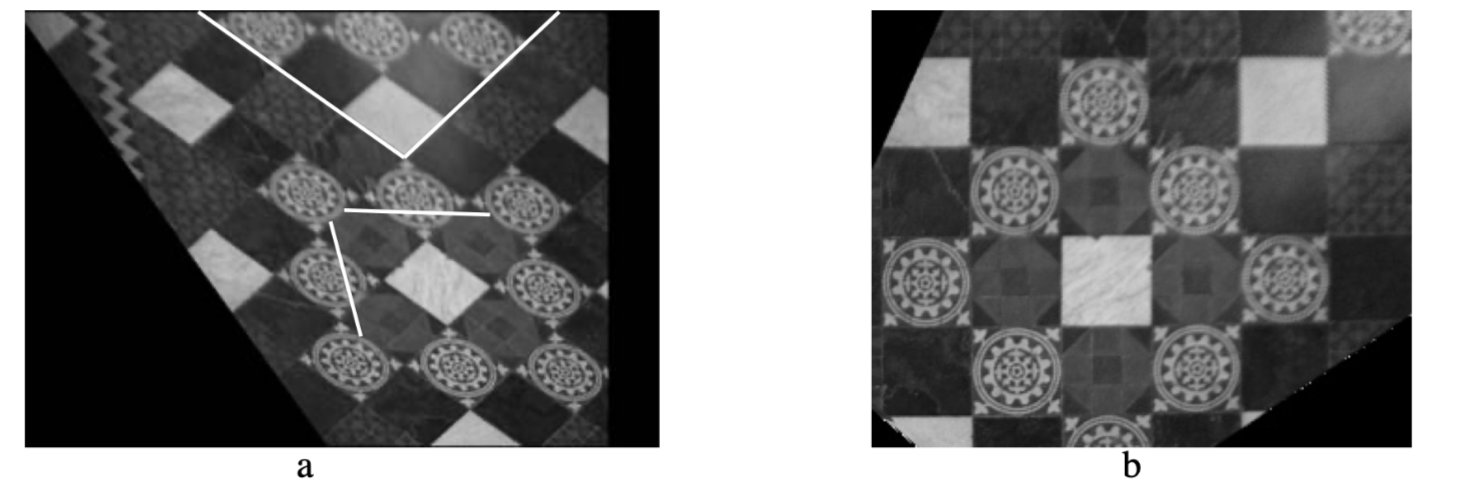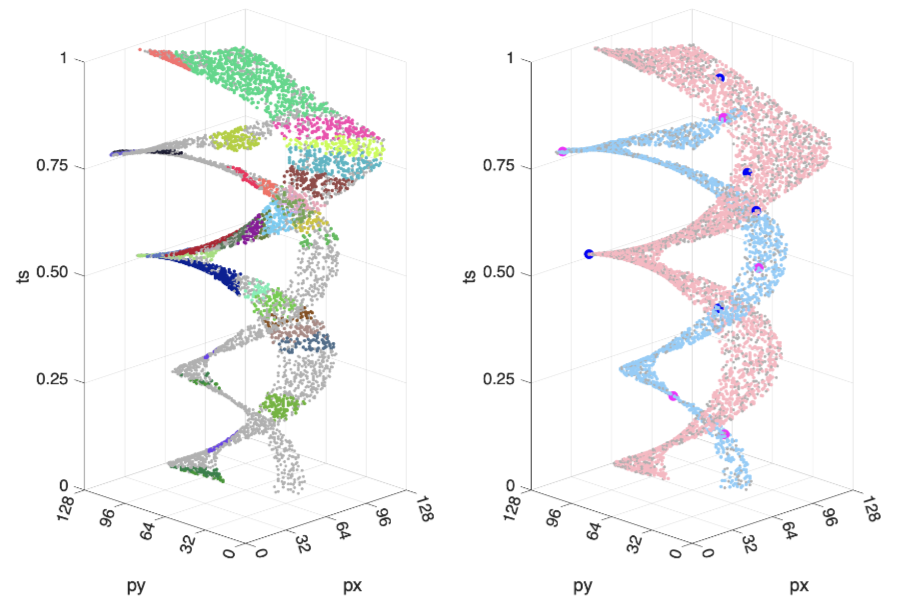
Reading:A 5-Point Minimal Solver for Event Camera Relative Motion Estimation
Original Paper Link:Paper
Paper Auther: Ling Gao* ,Hang Su* ,Daniel Gehrig, Marco Cannici, Davide Scaramuzza, Laurent Kneip
Preliminaries
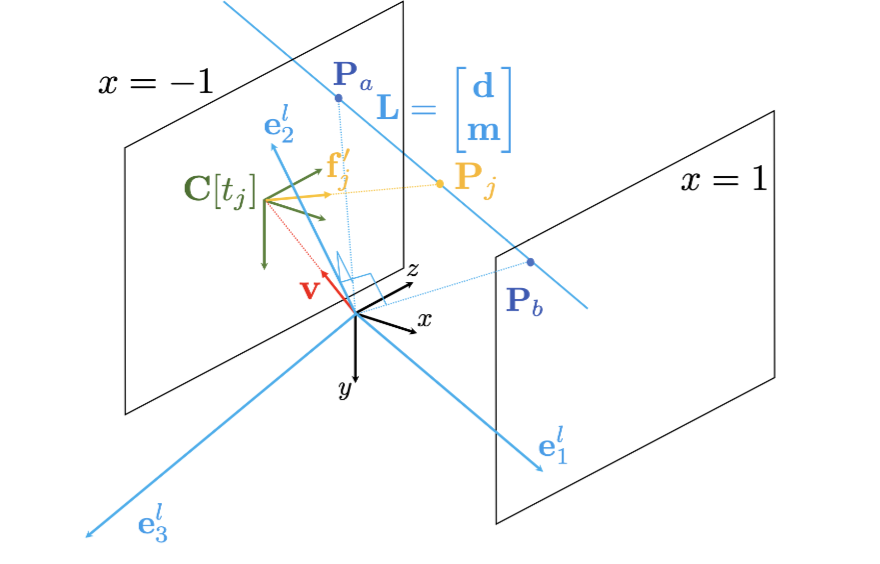
Plucker Coordinates
A Line L can be represented by its direction vector d and a point P
For two nonparallel lines
Event-based Data Notations
Consider data in
Function here projects points
Converesely have
And
Incidence Relationship
Camera center at time
Rotation from camera frame to reference frame
And we also have
Therefore, the ray can be described in plucker coordinates
$$\left( \left[ \mathbf{R}[t_{ij}] \mathbf{f}{ij} \right]^{\top} \left( \mathbf{C}[t{ij}] \times \left( \mathbf{R}[t_{ij}] \mathbf{f}{ij} \right) \right) \right)^{\top}
$$
Transition to Minimal Form
There are two points in the reference frame
And we define the base of three new directions
Since the velocity in x directions cannot be observed, we have
$$\mathbf{v} = \left[ \mathbf{e}_1^{\ell} \quad \mathbf{e}2^{\ell} \quad \mathbf{e}3^{\ell} \right] \cdot \left[ 0 \quad v_y^{\ell} \quad v_z^{\ell} \right]^{\top} = \mathbf{R}{\ell} \mathbf{v}{\ell}.
$$
Five Point Minimal Solver
To remove the scale invariance, an additional constraint on the scale is added. Given that only the structure parameters are affected by the scale invariance, the scale constraint needs to include the related variables. We constrain the scale by adding the equation
$$\left( \mathbf{R}{\ell} \mathbf{v}{\ell} \right)^{\top} \cdot \mathbf{R}{\ell} \mathbf{v}{\ell} - 1 = 0.
\mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{1i}^{\ell} \cdot \kappa_i + \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell} \cdot v{yi}^{\ell} + \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell} \cdot v_{zi}^{\ell} \
\mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{1i}^{\ell} \cdot \kappa_i + \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell} \cdot v{yi}^{\ell} + \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell} \cdot v_{zi}^{\ell}
\end{cases}
\Leftrightarrow
\begin{cases}
\mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = \left| \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell} \right|2^2 \cdot v{yi}^{\ell} \
\mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = \left| \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell} \right|2^2 \cdot v{zi}^{\ell}
\end{cases}
\Leftrightarrow
\begin{cases}
\left| \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{2i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = v{yi}^{\ell} \
\left| \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{3i}^{\ell \top} \mathbf{v} = v{zi}^{\ell}
\end{cases}.
\left| \mathbf{e}{21}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{21}^{\ell \top} & -v{y1}^{\ell} & \cdots & 0 \
\left| \mathbf{e}{31}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{31}^{\ell \top} & -v{z1}^{\ell} & \cdots & 0 \
\vdots & \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots \
\left| \mathbf{e}{2N}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{2N}^{\ell \top} & 0 & \cdots & -v{yN}^{\ell} \
\left| \mathbf{e}{3N}^{\ell} \right|2^{-2} \cdot \mathbf{e}{3N}^{\ell \top} & 0 & \cdots & -v{zN}^{\ell}
\end{bmatrix}
$$
- Title: Reading:A 5-Point Minimal Solver for Event Camera Relative Motion Estimation
- Author: Gavin0576
- Created at : 2024-06-02 22:26:25
- Updated at : 2024-07-14 10:03:52
- Link: https://jiangpf2022.github.io/2024/06/02/A-5-Point-Minimal-Solver-for-Event-Camera-Relative-Motion-Estimation/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.